Diving Deeper
In the previous section we got an understanding on how to setup a meta-framework based project for your local development and create a new project via cli commands. This section is dedicated to providing hands-on practice in constructing comprehensive backend services utilizing the meta framework and its associated plugins. Additionally, it aims to facilitate a thorough understanding of all the fundamental concepts underpinning the Godspeed framework.
Video Playlist for Detailed Walkthrough
Don't miss! Video Playlist of detailed guide to eventsources, events, functions and datasources: Watch here
Before we move forward
You may be in urging to move ahead quickly with trying out Godspeed Meta Framework, but wouldn't you first like to understand the WHY? Why you should try the Meta Framework?
Why we created the meta-framework? What tenets. design principles and guardrails we believe should be followed by every tech organisation?
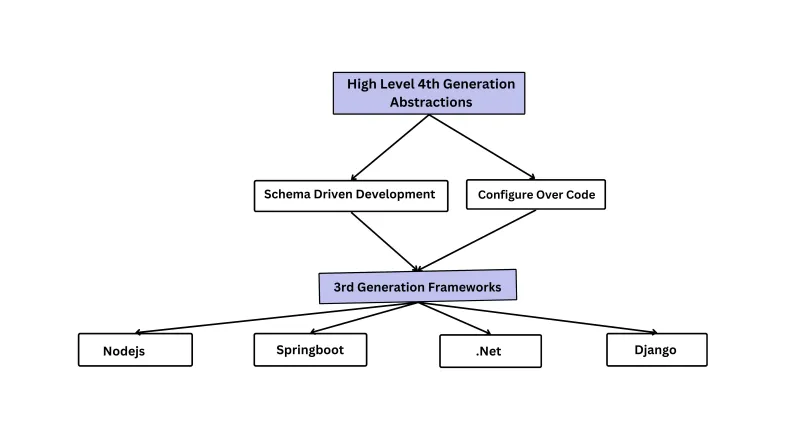
The three pillars
Have you seen the three pillars of abstraction in the Meta-Framework?
What is the benefit of adopting the Meta Framework's 4th generation engineering approach versus developing on pure Nodejs or Django stack (third generation frameworks) from scratch.
Moving forward
In getting started section we created a project that includes a simple 'hello world' example which uses an http Express eventsource, events and event handler functions.
Now we can move into further details.
In order to see detailed examples and documentation of an eventsources, events and event handlers please visit Express HTTP Eventsource Plugin documentation.
Event schema
Now lets understand how our helloworld api endpoint is working behind the scene
"./src/events/helloworld.yaml"
"http.get./helloworld":
fn: helloworld
Lets understand the first line from the above snippet http.get./helloworld: [know more]
http: Protocol http eventsource
get : method
/helloworld: endpoint
We are exposing an endpoint with a get method on http protocol. this endpoint is calling a workflow [a simple function ] fn: helloworld second line of the above code snippet.
Event Handler
Event handlers can be functions written in typescript, javascript or yaml DSL workflows. In the above example the helloworld function exists in src/functions directory. It could be helloworld.ts, helloworld.js or helloworld.yaml
Pure functions
Event handlers are pure functions which take input as JSON and return output as JSON, in a given standard format, independent of the eventsource from which the event originated. This is the fourth guardrail of the Meta Framework - Decoupled or Modular Architecture.
This allows reusability of the function code to expose it as handler via multiple eventsources, and also decouples the business logic with the eventsource, allowing you to
- Learn once how to develop business logic and patch handlers to any event source, reducing the learning curve and effort for adding new eventsources (Maintainability, reusability and democratisation)
- Replace an event source with another without affecting your implementation (Agility)
Sample typescript workflow
import { GSContext, PlainObject } from "@godspeedsystems/core";
export default function (ctx: GSContext, args: PlainObject) {
//Find more details about structure of GSContext in HTTP Express Eventsource Plugin page
// You return only the pure data, which is sent back in response by repsective eventsource, with data, code and headers
return { //GSStatus compativle return
data: 'Its working! ' + inputs.data.body?.name,
code: 200,
success: true,
headers: {
custom_response_header: 'something'
}
}
}
we are importing GSContext & GSStatus from core package of godspeed. go to their respective section to more about it.
Sample YAML workflow
id: helloworld
tasks:
- id: first_task
fn: com.gs.return
args:
data: <%'Its working! ' + inputs.body.name%>
code: 200
success: true #by default success is assumed to be true
headers:
custom_response_header: 'something'
The helloworld event is calling the above event handler workflow and executing a task from tasks with id first_task, which is then calling fn: com.gs.return function that takes argument name in an inline script.
So far we have seen how can we use Express plugin and also we created an endpoint which returns a response with some code and headers. Meta-framework make it easy for you to get started quickly saving your time setting everthing from scratch, and as well helps you do incremental development with best practices based guardrails.
JWT authentication
The Meta Framework currently supports standardised JWT authentication implementation across Express, Fastify and Apollo Graphql plugins.
Configure the eventsource to enable jwt authentication. More detailed information about authentication available here
"./src/eventsources/http.yaml"
type: express
jwt:
issuer: <#config.issues#> # must be equal to the key iss in your jwt token
audience: <#config.audience#> #must be equal to the key aud in your jwt token
secretOrKey: <#config.secret#>
This enables JWT authentication on all your endpoints for the given eventsource.
Disabling authentication on a given endpoint
You can disable authn on any endpoint by setting authn: false
"http.get./helloworld":
fn: helloworld
authn: false
Handling authorization
The Meta Framework gives you full freedom to handle authorization based on RBAC, ABAC or PBAC, in a generic way, independent of the event source.
It allows you to add authz configuration
- Unviersal or common authorization workflow at an eventsource instance level - for every event handled via that eventsource instance
- Disabling or customizing authorization at event level - you can disable authorization at an event level by saying
authz: falseor customize it by setting an authorization function or inline yaml workflow there itself
Swagger generation
See Swagger related configurations in http eventsource and event level both, in Express Plugin documentation
Your Swagger docs are automatically generated and stored in /docs folder when the project starts. The documentation is generated from a combination of settings in
- Eventsource level (refer the
docssection in http.yaml). This is applicable for Express and Fastify eventsources. - Event level
- When you enable authentication on an event, its security scheme is set accordingly in generated swagger. By default authentication is enabled on all events when enabled on eventsource instance level itself.
requestBody,params,responses,operationId,id,summary,descriptionare also picked up from event spec.
Graphql setup with schema generation
Check out the Apollo Graphql plugin documentation for more details.
CRUD API generation
Checkout how to generate CRUD APIs in a step by step guide.
Using Plugins
Checkout the available plugins for eventsources and datasources which allow you to get started with bunch of eventsources and datasources with simple configurations.
Reference Projects
For further learning resources and materials to kickstart your Godspeed development journey, please clone the gs-node-templates repository. This repository contains following examples for now.
- hello_world
- Full stack React based application
- Loan Origination System - the most complex example with fintech usecase
- Before running the LOS code, do read its setup.md file